What Is the Cosmetic Industry? Complete Overview from Manufacturing to Packaging and Dispatch
Introduction
The cosmetic industry covers everything from product concept creation to final dispatch of finished cosmetic products. It is not limited to mixing ingredients only. A professional cosmetic product goes through multiple controlled stages such as formulation, manufacturing, quality control, packaging, storage, and dispatch.
This article explains the complete cosmetic industry workflow, starting from manufacturing and ending at dispatch, in a simple and professional way.
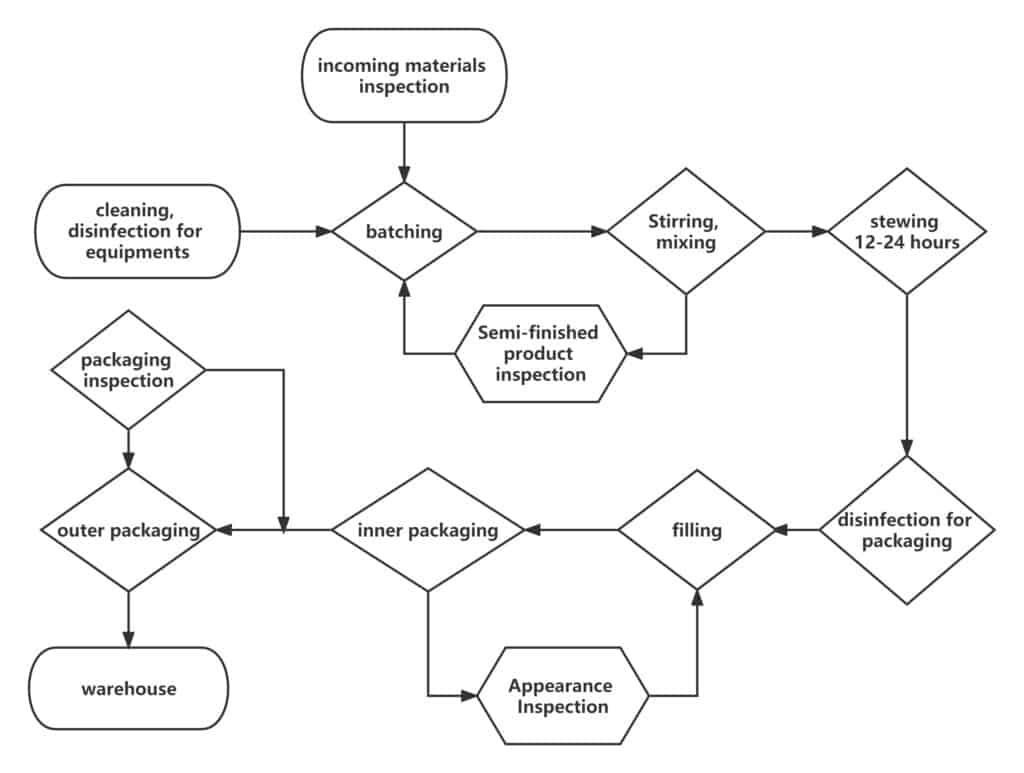
What Is the Cosmetic Industry?
The cosmetic industry includes companies and manufacturers involved in:
- Developing cosmetic formulations
- Manufacturing cosmetic products
- Packaging and labeling
- Storing and dispatching finished goods
Cosmetic products are designed for external use only and focus on cleansing, protecting, beautifying, or improving appearance.

Major Segments of the Cosmetic Industry
- Skincare products
- Haircare products
- Personal hygiene products
- Color cosmetics
Each segment follows a similar manufacturing-to-dispatch workflow, with minor technical differences.
Complete Cosmetic Manufacturing Process (Step-by-Step)
Step 1: Product Planning & Concept Development
Before manufacturing starts, planning is done for:
- Product type (cream, lotion, shampoo, serum, soap)
- Target users (men, women, baby, sensitive skin)
- Claims (herbal, sulfate-free, paraben-free)
- Texture, fragrance, and color preference
This stage decides commercial success or failure of the product.
Step 2: Raw Material Procurement & Approval
Only approved cosmetic-grade raw materials are selected, such as:
- Oils and butters
- Water-phase ingredients
- Emulsifiers
- Thickeners
- Preservatives
- Fragrances and colors
Each raw material is checked for:
- Certificate of Analysis (COA)
- Safety data
- Compatibility
Step 3: Cosmetic Formulation Development
Formulation is the backbone of cosmetic manufacturing and includes:
- Percentage calculation of ingredients
- Oil phase and water phase separation
- pH range selection
- Stability planning
Without a proper formulation, no cosmetic product can survive in the market.
Step 4: Manufacturing Process (Production Stage)

4.1 Preparation of Water Phase
Water-soluble ingredients are added
Heated to required temperature (usually 70–75°C)
4.2 Preparation of Oil Phase
Oils, waxes, emulsifiers are melted
Heated to the same temperature as water phase
4.3 Emulsification
Oil phase is slowly added to water phase
Mixing is done using a homogenizer or stirrer
4.4 Cooling Phase
- Batch is cooled gradually
- Heat-sensitive ingredients are added below 40°C
This step ensures stable and smooth texture.
Step 5: Quality Control (QC) & In-Process Testing
Quality control is mandatory at every stage.
Key Tests Include:
- pH testing
- Viscosity check
- Color and odor check
- Appearance and texture
- Microbial safety (if applicable)
❗ Without QC, products may fail in the market or get customer complaints.
Step 6: Filling Process (Bulk to Pack Conversion)
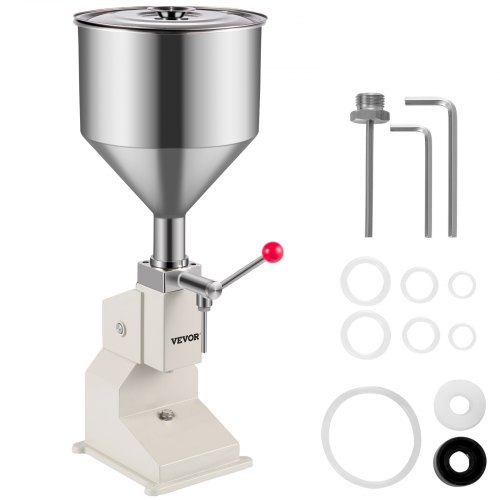

After QC approval, the product moves to filling.
Filling Includes:
- Selecting suitable containers (jar, bottle, tube)
- Using filling machines or manual filling
- Weight and volume accuracy check
- Leakage testing
This stage converts bulk product into saleable units.
Step 7: Packaging & Labeling
Packaging protects the product and provides legal information.
Primary Packaging
- Container holding the product (jar, bottle, tube)
Secondary Packaging
- Outer box or shrink wrap
Label Must Contain:
- Product name
- Ingredient list (INCI names)
- Batch number
- Manufacturing & expiry date
- Usage instructions
Incorrect labeling can lead to legal issues.
Step 8: Finished Goods Storage
After packaging, products are stored in controlled conditions.
Storage Guidelines:
- Clean and dry warehouse
- Controlled temperature
- FIFO system (First In, First Out)
- Batch-wise stacking
Improper storage can reduce shelf life.
Step 9: Dispatch & Logistics (Final Step)
Dispatch is the final stage of the cosmetic industry workflow.
Dispatch Process Includes:
- Order verification
- Invoice and documentation
- Secondary protective packing
- Transport mode selection (road, courier, freight)
Important Dispatch Points:
- Product safety during transport
- Avoid heat and leakage
- Proper carton labeling
- Tracking and delivery confirmation
Efficient dispatch ensures customer satisfaction and brand trust.
Why Manufacturing-to-Dispatch Control Is Important?
Complete control from manufacturing to dispatch ensures:
- Consistent product quality
- Reduced returns and complaints
- Legal compliance
- Strong brand reputation
Cosmetic Industry vs Random Homemade Products
| rofessional Cosmetic Industry | Homemade Mixing |
|---|
| Scientific formulation | No formulation |
| Quality control | No testing |
| Legal compliance | High risk |
| Shelf life stability | Unstable |
Conclusion
The cosmetic industry is a system-driven industry, not a random mixing process. From formulation and manufacturing to packaging, storage, and dispatch, every step must be properly controlled.
Understanding this complete workflow is essential for anyone planning to enter cosmetic manufacturing or private label business.