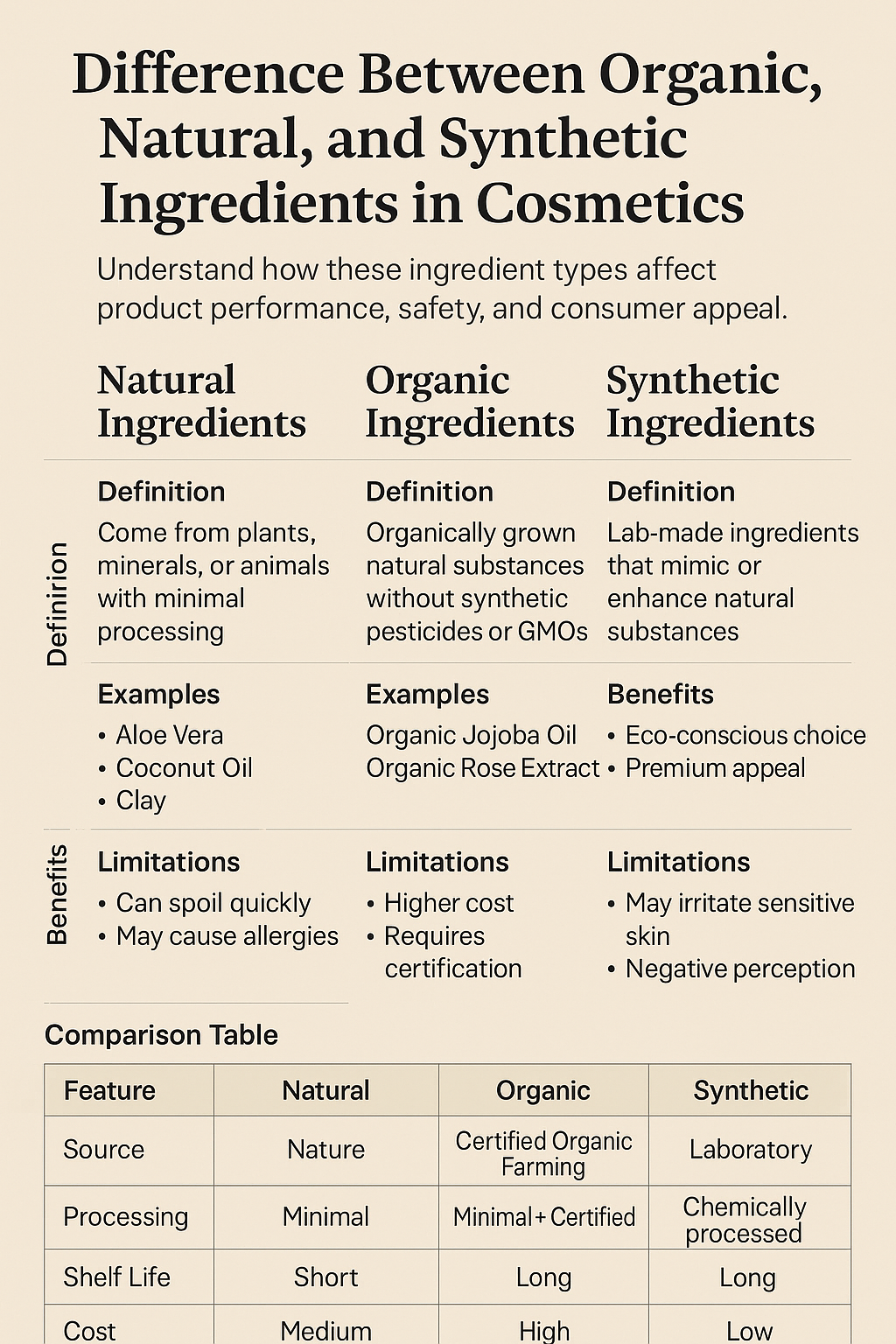
Understand how these ingredient types affect product performance, safety, and consumer appeal.*
Introduction
Cosmetic products are often labeled as organic, natural, or synthetic, but many consumers—and even professionals—are confused about what these terms truly mean. Understanding the difference between them is essential not just for compliance and marketing, but also for product development and consumer education. In this blog, we will explore the definitions, benefits, and concerns associated with each category of cosmetic ingredients.
1. Natural Ingredients
Definition:
Natural ingredients are derived directly from plants, minerals, or animals and are minimally processed. They are typically found in nature and used in cosmetics without synthetic modification.
Examples:
Aloe Vera
Coconut Oil
Honey
Clay
Shea Butter
Benefits:
Biodegradable and eco-friendly
Often gentle on the skin
Perceived as safer and healthier by consumers
Limitations:
May cause allergies
Shorter shelf life
Prone to contamination if not preserved properly
2. Organic Ingredients
Definition:
Organic ingredients are natural substances that are grown without the use of synthetic pesticides, fertilizers, or genetically modified organisms (GMOs). They must be certified by recognized bodies (like USDA, COSMOS, or ECOCERT).
Examples:
Certified Organic Jojoba Oil
Organic Rose Water
Organic Green Tea Extract
Benefits:
Safer for the environment and farm workers
May contain higher nutrient content
Marketed as premium and pure
Limitations:
More expensive to source
May still require preservatives
Limited availability in large-scale production
3. Synthetic Ingredients
Definition:
Synthetic ingredients are man-made compounds, often created in laboratories to mimic or improve upon natural substances.
Examples:
Parabens (Preservatives)
Silicones (e.g., Dimethicone)
Synthetic Fragrances
PEGs (Polyethylene Glycols)
Benefits:
More consistent quality
Longer shelf life
Cost-effective and scalable
Can be tailored for specific functions (e.g., anti-aging, UV protection)
Limitations:
May cause irritation or allergic reactions
Environmental concerns (e.g., non-biodegradability)
Negative perception among “green” consumers
Key Differences Table
Feature Natural Organic Synthetic
Source Nature Certified Organic Farming Laboratory
Processing Minimal Minimal + Certified Chemically processed
Shelf Life Short Short Long
Cost Medium High Low
Consumer Appeal High Very High Low to Moderate
Conclusion
Choosing between organic, natural, and synthetic ingredients depends on your brand’s goals, target audience, and formulation needs. While organic and natural products appeal to eco-conscious and health-aware consumers, synthetic ingredients offer stability and innovation. A balanced approach often works best—combining safe synthetics with high-quality natural extracts.