Quality Assurance Pharma 2025
Quality Assurance In the pharmaceutical industry, where human health and safety are top priorities
Quality Assurance (QA) plays a critical role in ensuring that medicines are safe, effective, and meet regulatory standards. QA is not just a department—it’s a philosophy and a systematic process that governs how pharmaceutical products are manufactured, tested, stored, and delivered.
This blog will provide a complete overview of the QA department in the pharmaceutical industry, including its roles, responsibilities, importance, and impact on regulatory compliance.
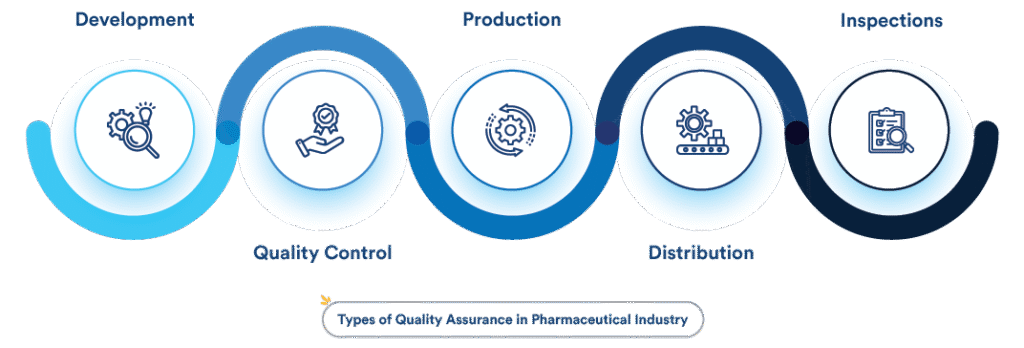
🔍 What is Quality Assurance (QA) in Pharma?
Quality Assurance in the pharmaceutical industry refers to a wide range of planned and systematic actions implemented within the quality system to ensure that a product meets the required quality standards.
Unlike Quality Control (QC)—which is about testing the final product—QA focuses on preventing errors throughout the manufacturing and development process by building quality into the system from the start.
🧩 Structure of QA Department
The QA department in a pharmaceutical company usually comprises several key subdivisions:
Documentation Team
Validation & Qualification Team
Auditing & Compliance Team
Training & SOP Monitoring
Change Control & Deviation Handling Team
Each of these plays a vital role in maintaining Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and other quality standards.
🎯 Key Responsibilities of the QA Department
1. Development and Management of SOPs
Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) are critical in the pharma industry. QA ensures:
SOPs are written clearly and in compliance with regulations.
Regular review and version control of SOPs.
Training staff on relevant SOPs.
2. Batch Record Review
QA is responsible for reviewing:
Batch Manufacturing Records (BMRs)
Batch Packaging Records (BPRs)
This ensures that every batch of medicine is traceable and manufactured correctly.
3. Deviation Management
Whenever a process deviates from the defined SOPs or batch records, QA must:
Investigate the deviation.
Identify root causes.
Implement corrective and preventive actions (CAPA).
4. Change Control
If a change in equipment, materials, or processes is necessary, QA ensures:
Proper documentation and approval.
Risk assessment and validation before implementation.
5. Training Programs
QA conducts and tracks employee training to ensure that:
Staff is competent in GMP and job functions.
Training records are up to date.
6. Self-Inspections and Audits
QA plans and executes:
Internal audits
Supplier audits
Third-party inspections
Findings are documented and followed up with CAPAs.
7. Validation and Qualification
QA is responsible for:
Process Validation
Equipment Qualification
Cleaning Validation
These activities ensure consistent and reliable output.
8. Regulatory Compliance
QA ensures compliance with:
WHO-GMP
USFDA
MHRA
EMA
CDSCO
QA prepares the company for inspections and maintains readiness for audits.
9. Quality Risk Management
QA assesses the risks associated with each process and implements control strategies to minimize them.
📜 Importance of QA in the Pharmaceutical Industry
Patient Safety
Medicines must be free from contamination and must contain the correct strength. QA ensures this through robust systems.Regulatory Compliance
A strong QA system avoids legal issues and regulatory penalties.Market Authorization and Product Approval
Drugs must meet stringent quality guidelines to be approved by global agencies. QA supports dossier preparation and technical files.Brand Reputation
A poor-quality product can damage a company’s image. QA ensures consistent product quality.Cost Efficiency
By preventing errors rather than correcting them later, QA saves time and money.
🏢 Common Roles in QA Department
| Role | Responsibility |
|---|---|
| QA Executive | Daily document review, deviation handling |
| QA Officer | SOP preparation, batch record review |
| QA Manager | Overall supervision, audit readiness |
| QA Auditor | Conduct internal/external audits |
| Validation Engineer (QA) | Oversee validation and qualification activities |
| Aspect | QA (Quality Assurance) | QC (Quality Control) |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Process-oriented | Product-oriented |
| Approach | Preventive | Corrective |
| Responsibility | Entire production lifecycle | Final product testing |
| Activities | SOPs, audits, training, validation | Sampling, lab testing, reporting |
📅 Day-to-Day Activities of QA Department
Morning review meetings
Cross-checking BMRs and BPRs
Monitoring cleanroom environment data
Validating new cleaning methods or processes
Preparing for audits
CAPA follow-up and documentation
Ensuring online documentation at every step
🌍 Global Standards QA Adheres To
ICH Guidelines
21 CFR Part 11 (USFDA)
WHO GMP
PIC/S
EU GMP Annexures
QA ensures the company’s systems align with international quality and safety standards.
🧠 Skills Required for QA Professionals
Attention to detail
Regulatory knowledge
Communication and documentation
Problem-solving ability
Audit preparedness
Strong understanding of manufacturing processes
📈 Challenges Faced by QA Teams
Keeping up with regulatory updates
Managing large volumes of documentation
Ensuring consistent training across departments
Root cause analysis for recurring deviations
Digital transformation and compliance with e-record systems
✅ Future of QA in Pharma
The future of QA is becoming more digitized and data-driven:
Use of AI for quality trend analysis
Digital QMS (Quality Management Systems)
Real-time batch record reviews
Focus on data integrity and cybersecurity
📌 Conclusion
The QA department is the backbone of the pharmaceutical industry, ensuring that every drug manufactured is safe, effective, and meets global standards. From managing SOPs to conducting audits and training employees, QA is deeply involved at every stage of drug development and manufacturing.
Pharmaceutical companies that invest in a robust QA system are more likely to build trust, avoid recalls, pass regulatory audits, and maintain a competitive edge in the global market.